
Responsive vs. adaptive: Which path leads to website success?
Discover the design decisions that determine your website's performance. This comparison will show you the advantages and disadvantages of adaptive and responsive design.
Future
Glossary
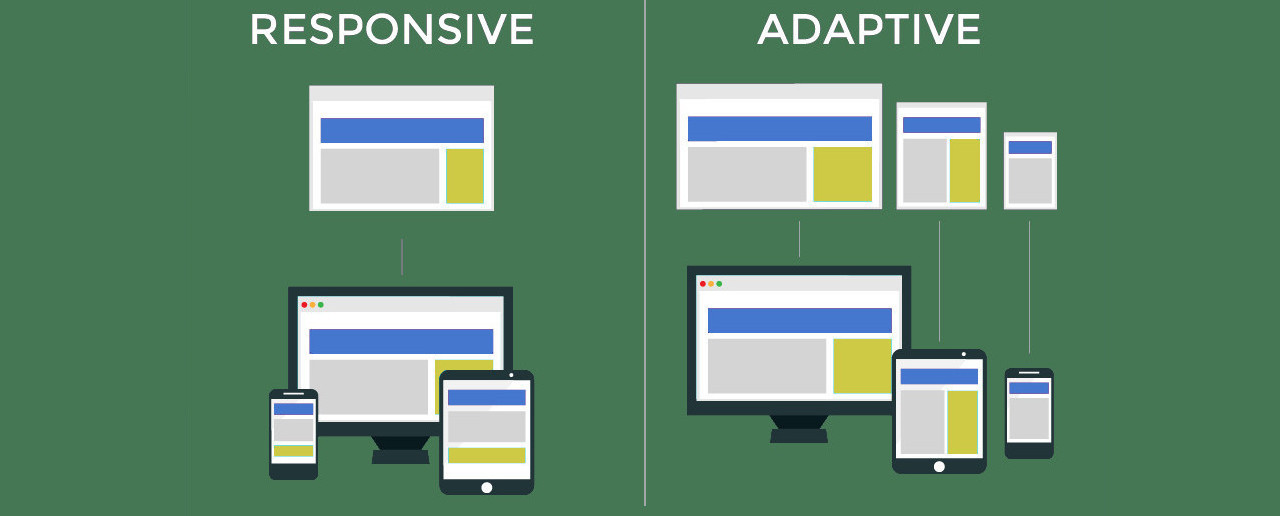
Responsive or adaptive?
Web design constantly evolves, and ensuring your website functions well on different devices is crucial. Due to the wide variety of screen sizes and resolutions on smartphones, tablets, laptops, and desktops, web designers must optimize the user experience for this vast digital landscape. To meet this challenge, there are two main approaches: responsive design and adaptable design. Each has its advantages and is suitable for different scenarios. Choosing between them can be a difficult decision, both for designers and website owners.
Responsive design: fluidity and flexibility
Responsive web design is a design approach that aims to create a seamless user experience across all devices by fluidly adapting the layout and content of a website to fit different screen sizes and resolutions. It achieves this through flexible grids, media queries, and CSS styling techniques. Responsive design is often considered a "one-size-fits-all" solution because it involves a single website that dynamically adjusts its appearance based on the device's characteristics.
- Fluid grids: Responsive designs use fluid grids to resize the page elements proportionally to fit within the screen space. This allows for a consistent experience across devices.
- Media Queries: CSS media queries are used to apply styles and layouts depending on a device's screen size and orientation. The content will be presented in the best way possible for every device.
- Cost-Effective: Responsive design can be cost-effective, as it only requires creating and maintaining one website. All updates and changes will be applied.
- Better SEO: Google recommends responsive designs as they simplify the crawling and indexing of your website, which could lead to a better search engine ranking.
Adaptive Design: tailored experiences
Adaptive web design takes a different approach by creating multiple versions of a website, each optimized for specific device categories or screen sizes. When a user accesses the website, server-side scripts detect the user's device and serve the appropriate version of the site. This approach offers high customization and control over the user experience.
- Device-Specified Versions: This is a device-specific version of a web page. It involves creating versions for different devices (such as mobile phones, tablets, or desktops). Each version is tailored to the unique capabilities and restrictions of the targeted device.
- Improved Performance: Adaptive designs are tailored to specific devices and can provide faster loading times, so they offer better performance.
- Complicated Implementation: Building and maintaining several versions of the same website is more resource-intensive. This can make it more expensive.
- Highly Customizable: This allows you to customize the user interface, which is ideal for complex websites or those with special requirements.
Choosing between responsive and adaptive design
The choice between responsive and adaptive design depends on various factors, including your website's goals, target audience, content complexity, and budget:
- Responsive web design can be a good choice for many websites offering consistent user-experience across all devices. It's cost-effective and aligns with SEO practices.
- Adaptive designs are ideal for projects requiring high customization levels and specific performance requirements. It is perfect for projects in which user experience optimization takes priority.
The final decision should be based on understanding your site's objectives and unique needs. Many websites employ a mixture of both approaches, allowing them to benefit from the best of both. Whatever route you choose, it's crucial to ensure that your site visitors have a positive experience, no matter the device on which they access your site.





